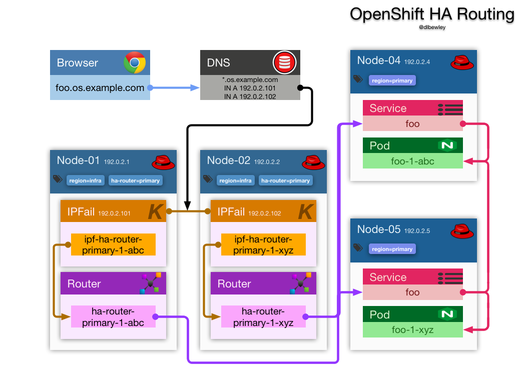
I needed to host a service that would be consumed by a closed client that insists on speaking HTTPS on port 50,000. To solve this, I added a 2nd router deployment and used the OpenShift router sharding feature to selectively enable routes on the 2nd router by way of selectors.
To summarize:
Existing HA router:
- HTTP 80
- HTTPS 443
- Haproxy Stats 1,936
Added HA router:
- HTTP 49,999
- HTTPS 50,000
- Haproxy Stats 51,936
How To
Open infra node firewalls
- Open firewall on infra nodes where router will run to allow new http and https port
iptables -A OS_FIREWALL_ALLOW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 49999 -j ACCEPT
iptables -A OS_FIREWALL_ALLOW -m tcp -p tcp --dport 50000 -j ACCEPT
- This can also be done with Ansible and the os_firewall role in your playbook. (untested)
- hosts: infra-nodes
vars:
os_firewall_use_firewalld: False
os_firewall_allow:
- service: teradici-http
port: 49999/tcp
- service: teradici-https
port: 50000/tcp
roles:
- os_firewall
Create a router
- Create a router called ha-router-teradici with
oa adm router or oadm router on these ports and also make sure the stats port does not clash with existing router on port 1936
[root@ose-test-master-01 ~]# oc get nodes --show-labels
NAME STATUS AGE LABELS
ose-test-master-01.example.com Ready 180d kubernetes.io/hostname=ose-test-master-01.example.com,region=master,zone=rhev
ose-test-master-02.example.com Ready 180d kubernetes.io/hostname=ose-test-master-02.example.com,region=master,zone=rhev
ose-test-node-01.example.com Ready 180d ha-router=primary,kubernetes.io/hostname=ose-test-node-01.example.com,region=infra,zone=rhev
ose-test-node-02.example.com Ready 180d ha-router=primary,kubernetes.io/hostname=ose-test-node-02.example.com,region=infra,zone=rhev
ose-test-node-03.example.com Ready 180d kubernetes.io/hostname=ose-test-node-03.example.com,region=primary,zone=rhev
ose-test-node-04.example.com Ready 180d kubernetes.io/hostname=ose-test-node-04.example.com,region=primary,zone=rhev
[root@ose-test-master-01 ~]# oadm router ha-router-teradici \
--ports='49999:49999,50000:50000' \
--stats-port=51936 \
--replicas=2 \
--selector="ha-router=primary" \
--selector="region=infra" \
--labels="ha-router=teradici" \
--default-cert=201602_router_wildcard.os.example.com.pem \
--service-account=router
GOOD: I see that the ports are set properly in the haproxy.config and the service objects
Continue reading